Most Cost Effective Siding A Homeowners Guide
Most cost effective siding doesn’t have to mean sacrificing quality or aesthetics. This guide dives into the world of affordable exterior cladding, exploring various materials like vinyl, fiber cement, and engineered wood, weighing their initial costs against long-term maintenance and lifespan. We’ll examine how factors like climate, location, and DIY versus professional installation impact the final price, helping you make an informed decision that fits your budget and home’s needs. Understanding the true cost, including labor, permits, and energy efficiency, is key to selecting the most financially sound option for your home improvement project.
From comparing insulation properties and exploring the potential of recycled materials to navigating contractor quotes and negotiating prices, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to choose the best siding for your home without breaking the bank. We’ll also delve into the long-term implications of your choice, considering its impact on your home’s resale value and energy costs over the years. This comprehensive approach will empower you to make a smart, cost-effective choice that enhances your home’s beauty and value for years to come.
Types of Cost-Effective Siding

Source: homeisd.com
Choosing the right siding can significantly impact a home’s curb appeal and long-term cost. This section will delve into the specifics of several cost-effective siding options, comparing their initial investment, maintenance requirements, and longevity. Understanding these factors is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your budget and lifestyle.
Vinyl, Fiber Cement, and Engineered Wood Siding Comparison
The following table compares three popular siding choices: vinyl, fiber cement, and engineered wood. Remember that prices can vary based on location, quality, and installation costs. This table provides a general overview for comparative purposes.
| Siding Type | Initial Cost | Maintenance | Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Low to Moderate | Low; occasional cleaning | 20-40 years |
| Fiber Cement | Moderate to High | Moderate; occasional painting and cleaning | 50-80 years |
| Engineered Wood | Moderate | Moderate to High; requires regular painting and sealing | 30-50 years |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Recycled or Reclaimed Siding Materials
Using recycled or reclaimed materials offers environmental benefits and can sometimes be more cost-effective than new materials. However, it’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons before making a decision.
Advantages: Reclaimed materials, such as salvaged wood siding from older buildings or recycled plastic lumber, contribute to sustainability by reducing waste and conserving resources. They often possess a unique character and charm, adding a distinctive aesthetic to a home. Depending on the source and condition, reclaimed materials can sometimes be cheaper than new options.
Disadvantages: Sourcing and preparing reclaimed materials can be more time-consuming and labor-intensive than purchasing new siding. The availability of specific types of reclaimed materials may be limited, and their condition can vary greatly, potentially requiring more extensive repairs or preparation before installation. The longevity and durability of reclaimed materials can also be less predictable compared to new, manufactured siding. Examples of reclaimed siding materials include salvaged wood planks (e.g., barn wood) and recycled plastic lumber made from post-consumer plastics.
Insulation Properties of Different Siding Types and Their Impact on Energy Costs
The insulating properties of siding materials directly affect a home’s energy efficiency and heating/cooling costs. Siding with higher R-values (a measure of thermal resistance) offers better insulation.
| Siding Type | R-Value (Approximate) | Impact on Energy Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | 0.00 – 0.06 | Minimal insulation; increased energy costs |
| Fiber Cement | 0.00 – 0.06 | Minimal insulation; increased energy costs |
| Engineered Wood | 0.00 – 0.06 | Minimal insulation; increased energy costs |
Note: The R-value of siding itself is generally low. The overall insulation of a home’s exterior wall system depends significantly on the insulation within the wall cavity (e.g., fiberglass batt insulation, spray foam insulation) rather than the siding material itself. Therefore, while siding contributes minimally to insulation, selecting materials that allow for better air sealing can still indirectly improve energy efficiency.
Factors Influencing Siding Costs
The total cost of siding installation is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, making it crucial to understand these elements before embarking on a project. A thorough understanding will allow for better budgeting and informed decision-making. This section breaks down the key cost components and explores how various factors impact the final price.
Cost Breakdown of Siding Installation
The total cost of siding installation can be divided into three main components: materials, labor, and permits. Let’s illustrate this with a hypothetical example of installing 1,500 square feet of vinyl siding on a single-family home.
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $4,500 | This includes the cost of the vinyl siding itself, underlayment, flashing, trim, and fasteners. Prices vary widely depending on the quality and features of the chosen siding. Higher-end vinyl siding with added features like thicker profiles or improved color retention will cost more. |
| Labor | $6,000 | Labor costs are heavily influenced by factors such as the complexity of the job, the size of the house, and the experience of the contractor. This estimate accounts for the time required for preparation, installation, and cleanup. |
| Permits | $500 | Permitting costs vary significantly by location. This estimate is a general average, but it’s essential to check with your local authorities for accurate costs. Some areas might require additional inspections, leading to higher fees. |
| Total Estimated Cost | $11,000 | This is a rough estimate, and the actual cost can vary significantly based on the factors discussed below. |
Climate and Geographic Location Impact
Climate and geographic location significantly impact siding material selection and overall cost. Materials suitable for one region may be unsuitable or significantly more expensive in another.
For example, in regions with harsh winters and heavy snowfall, such as the Northeast United States and Canada, durable and weather-resistant materials like fiber cement or engineered wood siding are often preferred. These options are typically more expensive than vinyl siding but offer superior longevity and protection against extreme weather conditions. Conversely, in milder climates like the Southeast, where humidity is a significant concern, vinyl siding or aluminum siding might be more cost-effective choices due to their resistance to moisture damage. In arid regions of the Southwest, where intense sun is a major factor, materials with high UV resistance, such as certain types of vinyl or painted fiber cement, are generally favored.
Key Factors Influencing Labor Costs
Three key factors significantly influence the labor costs associated with siding installation: the complexity of the project, the size of the house, and the contractor’s experience and reputation.
The complexity of the project refers to the presence of architectural details such as dormers, multiple rooflines, or intricate trim work. These details require additional time and skill, leading to higher labor costs. A larger house naturally requires more time for installation, leading to higher overall labor expenses. Finally, experienced and reputable contractors often charge more per hour than less experienced ones, but their expertise and efficiency can often result in better quality work and fewer potential problems down the line, potentially saving money in the long run.
DIY vs. Professional Installation: Most Cost Effective Siding
Choosing between DIY siding installation and hiring professionals significantly impacts the overall cost-effectiveness of your project. Several factors must be considered to determine the best approach for your specific circumstances and skills. While DIY can seem appealing for saving money upfront, unforeseen complications can quickly negate any initial cost savings.
This section will compare the cost-effectiveness of both options, detailing the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. We’ll also provide a list of necessary tools and materials for a small DIY project, along with an estimation of their costs. Finally, we’ll discuss potential risks and challenges associated with DIY siding installation.
DIY vs. Professional Installation Cost Comparison
The decision to tackle siding installation yourself or hire a professional hinges on a careful evaluation of several key factors. Consider these points when weighing your options:
- Time Investment: DIY installation requires a substantial time commitment. Professionals can complete the job much faster, allowing you to focus on other tasks. A small area might take a weekend for a skilled DIYer, but a larger area could take several weeks, depending on your experience and the weather.
- Material Waste: Professionals generally have more experience accurately measuring and cutting materials, minimizing waste. DIYers may miscalculate, leading to higher material costs.
- Potential Errors: Improper installation can lead to costly repairs, water damage, and even structural issues. Professionals possess the expertise to avoid these mistakes, minimizing long-term expenses. A poorly installed section might require complete replacement.
- Warranty Implications: Many siding manufacturers offer warranties that are often voided if the installation isn’t performed by a certified installer. Using a professional ensures warranty protection.
- Labor Costs: While professional installation has an upfront cost, it often balances out the potential for costly DIY errors and the value of your time.
Tools and Materials for a Small DIY Siding Project
For a small DIY siding project, such as replacing a few damaged panels, you’ll need specific tools and materials. Accurate estimation of quantities is crucial to avoid unnecessary expenses. The following list provides estimates for a small area (approximately 100 square feet), and costs are approximate and may vary depending on location and brand.
- Siding Panels (e.g., vinyl): Approximately 100 sq ft; $500 – $1000 (depending on material and style)
- Measuring Tape: $10
- Circular Saw or Jigsaws: $50 – $150 (If you don’t already own one)
- Hammer: $10 (If you don’t already own one)
- Nail Gun (optional, but recommended): $100 – $200
- Safety Glasses: $10
- Work Gloves: $10
- Caulk: $15
- J-Channel and Trim: $50 – $100
- Flashing: $20 – $50
Total Estimated Cost (excluding existing tools): $805 – $1530
Potential Risks and Challenges of DIY Siding Installation
DIY siding installation presents several potential risks and challenges that should be carefully considered. These include safety hazards and the potential for significant damage if not executed correctly.
- Falls from heights: Working at heights increases the risk of falls, potentially leading to serious injuries. Appropriate safety measures, such as scaffolding or ladders, are essential.
- Power tool injuries: Improper use of power tools, such as circular saws and nail guns, can cause severe injuries. Always follow safety instructions and wear appropriate protective gear.
- Material damage: Incorrect cutting or installation can damage siding panels, requiring replacements and increasing costs. Precise measurements and careful handling are crucial.
- Water damage: Improper installation can lead to water intrusion, causing rot, mold, and structural damage. This can be extremely costly to repair.
- Structural damage: Incorrect installation can compromise the structural integrity of the building, leading to further damage and significant repair costs. For example, incorrect installation of flashing can cause water damage that eventually leads to structural problems.
Long-Term Cost Considerations

Source: prosuperiorconstruction.com
Choosing siding isn’t just about upfront costs; long-term expenses significantly impact the overall value proposition. Factors like maintenance, repair needs, energy efficiency, and impact on resale value should be carefully considered before making a final decision. This section will delve into these crucial long-term cost implications to help you make an informed choice.
Siding Maintenance Requirements Over 20 Years
Proper maintenance is vital to extending the lifespan of your siding and preventing costly repairs. Different materials require varying levels of upkeep. Ignoring maintenance can lead to premature deterioration and necessitate expensive replacements. The following table compares the maintenance needs of several common siding types over a 20-year period. Note that these are estimates and actual costs can vary based on climate, exposure, and individual home maintenance practices.
| Siding Type | Cleaning (Frequency & Cost) | Repairs (Frequency & Estimated Cost) | Potential Replacement (Year & Estimated Cost) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Annual cleaning (low cost); occasional power washing | Infrequent minor repairs (low cost); possible replacement of damaged panels | 15-20 years ($5,000 – $15,000) |
| Fiber Cement | Periodic cleaning (moderate cost); occasional repainting | Occasional repairs (moderate cost); potential caulking | 25-30 years ($7,000 – $20,000) |
| Wood | Regular cleaning and staining/sealing (high cost) | Frequent repairs (high cost); potential pest control | 10-15 years ($8,000 – $25,000+) |
| Aluminum | Periodic cleaning (low cost) | Infrequent repairs (low-moderate cost); potential dent repair | 20-30 years ($6,000 – $18,000) |
Impact of Siding on Resale Value
The type of siding you choose can significantly influence your home’s resale value. Buyers often associate certain siding materials with higher quality, better curb appeal, and lower maintenance. For instance, fiber cement siding is often viewed favorably due to its durability and low-maintenance nature, potentially commanding a higher price. Conversely, older, damaged wood siding might negatively impact the value. High-quality vinyl siding, properly installed and maintained, can also contribute positively to resale value. The overall condition of the siding, regardless of the material, is paramount.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings, Most cost effective siding
Siding plays a role in your home’s energy efficiency. Materials with higher insulation values can reduce heating and cooling costs over time. While the initial cost of more energy-efficient siding might be higher, the long-term savings can offset this investment. The following table provides a comparison, noting that actual savings will depend on factors such as climate, home size, and existing insulation. These figures are estimates based on average scenarios.
| Siding Type | Initial Energy Cost (Increased Installation Cost) | Long-Term Energy Savings (Over 20 Years) | Overall Energy Cost (Initial + Energy Savings) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Fiber Cement | Moderate | High | High |
| Wood | High | Moderate (with proper insulation) | High (depending on insulation and maintenance) |
| Aluminum | Low | Low | Low |
Finding Cost-Effective Contractors
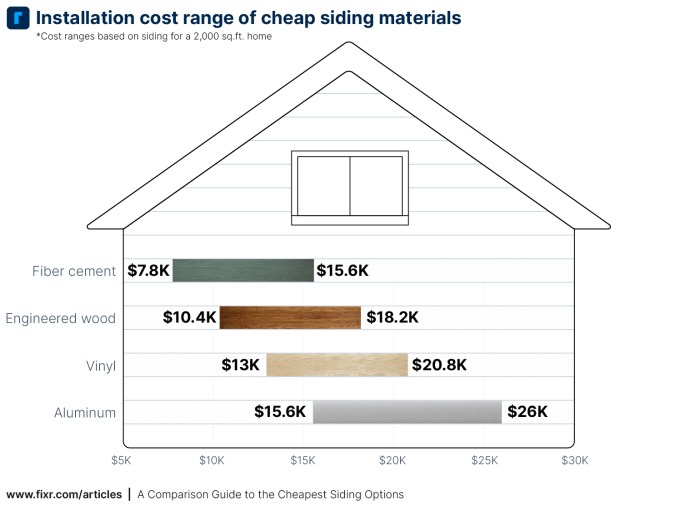
Source: fixr.com
Securing a skilled and reasonably priced siding contractor is crucial for a successful and budget-friendly project. This involves a multi-step process that combines thorough research, careful vetting, and strategic negotiation. By following these steps, you can significantly increase your chances of finding a contractor who meets your needs and your budget.
Finding a reputable and reasonably priced siding contractor requires a systematic approach. This involves leveraging various resources, verifying credentials, and comparing quotes to ensure you’re getting the best value for your investment. Negotiation plays a key role in securing favorable terms and potentially saving money.
Contractor Research and Selection Methods
Several avenues exist for locating potential contractors. Online directories, such as those provided by the National Association of the Remodeling Industry (NARI) or Angie’s List (now part of HomeAdvisor), offer contractor profiles with reviews and ratings. Local referrals from friends, family, or neighbors can also be valuable, providing firsthand accounts of contractor performance. Checking with your local building supply stores can also yield recommendations. Finally, browsing online reviews on platforms like Google My Business or Yelp can offer insights into customer experiences. Remember to cross-reference information from multiple sources to build a comprehensive picture of each contractor.
Obtaining and Comparing Quotes
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential contractors, request detailed, written quotes. Ensure these quotes include a comprehensive breakdown of materials, labor costs, permits, and any other associated expenses. Don’t hesitate to ask for clarification on any unclear items. Direct comparison of these quotes, item by item, will allow you to assess the value proposition of each contractor. Note that the lowest bid isn’t always the best option; consider the overall value offered, including experience, warranties, and materials quality.
Verifying Contractor Credentials and Insurance
Before committing to a contractor, verify their credentials. Request proof of licensing and insurance, including workers’ compensation and general liability insurance. These documents protect you from potential liabilities should accidents occur during the project. Check with your state’s licensing board to confirm the contractor’s license is valid and up-to-date. Also, inquire about the contractor’s experience with similar projects and request references you can contact to discuss their past performance.
Negotiating Prices and Payment Plans
Negotiating with contractors is a common practice. Start by clearly stating your budget and exploring options for reducing costs. This might involve discussing alternative materials, adjusting the scope of work, or exploring phased payment plans. Be polite but firm in your negotiations. Don’t be afraid to walk away if you’re not comfortable with the proposed terms. Remember that reputable contractors are often willing to work with you to reach a mutually agreeable price. For example, you could propose a slightly lower price in exchange for a quicker project completion or a favorable payment schedule.
Checklist of Questions for Potential Contractors
A well-structured set of questions will help you evaluate potential contractors effectively. Asking about their experience with specific siding types, their process for handling unforeseen issues, and the details of their warranties will provide valuable insights. Inquire about their payment schedule, including whether they require a down payment and the payment terms for the remainder of the project. Understanding their approach to project management and communication is also vital. Finally, explicitly asking about their cost-effectiveness strategy, focusing on material sourcing and labor efficiency, will ensure alignment with your budget goals.
Concluding Remarks
Ultimately, choosing the most cost-effective siding involves a careful balancing act between upfront costs, long-term maintenance, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. By understanding the various factors influencing the total cost—from material selection and installation to ongoing maintenance and potential resale value—you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your budget and long-term goals. Remember to thoroughly research materials, get multiple quotes from reputable contractors, and factor in all associated costs before making your final choice. A little planning now can lead to significant savings and a beautiful, durable exterior for years to come.
Top FAQs
What is the average lifespan of vinyl siding?
Vinyl siding typically lasts 20-30 years, depending on quality and maintenance.
Can I install siding myself, or should I hire a professional?
While DIY is possible for small areas, professional installation often offers better results, warranty protection, and avoids potential costly mistakes.
How much does a siding permit typically cost?
Permit costs vary widely by location. Check with your local building department for accurate pricing.
What are some signs that my siding needs to be replaced?
Signs include significant damage, rotting, warping, discoloration, or excessive cracking.
Are there tax credits or rebates available for energy-efficient siding?
Check with your local and state government websites for potential energy-efficiency incentives.





